CloudLogger SCADA
analysisNodal
Methodology that allows evaluating the performance of the Integrated Production System (SIP), in accordance with current operating conditions. And if it is necessary to optimize, it allows you to create scenarios.


What does it consist of
Nodal Analysis
It consists of isolating the system in two sections using nodes and selecting a solution node to calculate the pressure drops in each of them. This quantifies the impact of each of its elements and determines which ones to optimize.
The data monitored by telemetry can be linked as input data.
What does the
Nodal Analysis
Currently it is solved using the downhole as a solution node, for which there are two sections in which the flow of fluids is simulated.

Deposit
Darcy Inflow Model.
Well and surface facilities
Hagedorn and Brown Correlation Modified.

Application
- Flowing wells
- Pneumatic Pumping Wells
SUBMODULOS
Within this module there are submodules, in which input data that is not available and additional data can be calculated according to user requirements.

Damage factor

Efficiency curve
Operating valve
Which can be linked as input data in the corresponding system section.
Capital Analysis
Performance evaluation
CURRENT AND FUTURE
Assessment of current and future performance according to the operating conditions of the well and the reservoir to obtain the production potential.

The system is divided into solution nodes and the results are visualized in a graph of expense vs. pressure.

CloudLoggerSCADA ™ allows you to link data in real time for analysis.

Cloudlogger – scada – nodal analysis
Efficiency curve
Pneumatic pumping works by injecting a certain amount of gas continuously or intermittently as deep as possible into the fluid column through a valve anchored in the production pipeline, with the purpose of reducing the flowing pressure at the bottom of the well, increasing the pressure differential across the drain area so that the producing formation increases the production rate that it delivers to the well.
- The volume of gas supplied to the production line during the injection period is approximately that required to fill the line with the compressed gas from the annular space.
- Surface operating conditions are a very important factor in the volume of gas required.
- The module currently has a sensitization method applied to injection gas in wells with pneumatic pumping, using the nodal analysis module to perform the calculations.
- The results are presented using a graph of injected gas vs. expense.
Nodal Analysis – cloudlogger
Total damage (S)
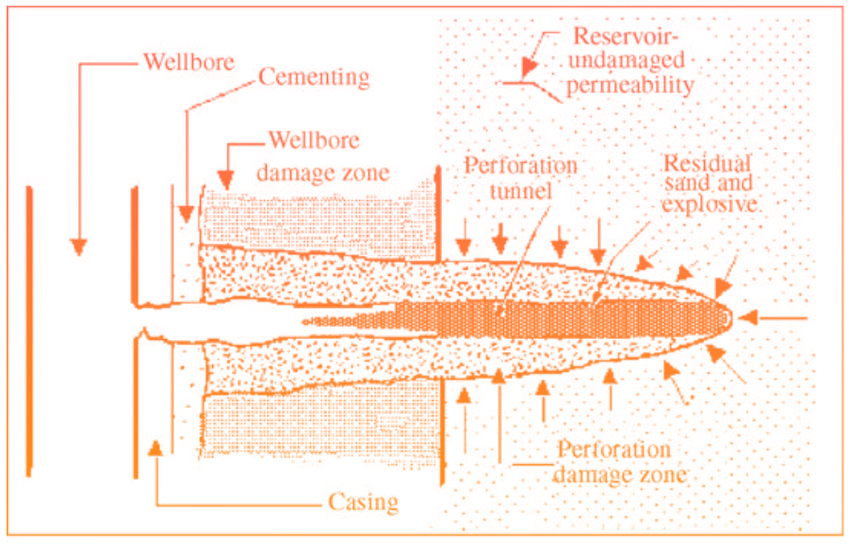
It is a dimensionless value and is any partial or total restriction of the flow lines from the reservoir to the downhole. This is caused by the alteration that an isolated static medium undergoes, such as the storage rock when interacting with a dynamic medium, which is represented by all the operational processes, such as drilling, cementing, firing and production.
If the value of this parameter is not available, this module is made available to the user.
Once the value of this parameter is obtained, it will be linked to the input data in the reservoir section to perform the Nodal Analysis calculation.
- Sensitization applied to injection gas in wells with pneumatic pumping.
- The optimal amount of gas to be injected is determined to obtain a greater production of hydrocarbons.
- The implementation of the results is reflected in the economic part of the project.





Formation Damage (S)
It is a dimensionless value and is any partial or total restriction of the flow lines from the reservoir to the downhole. This is caused by the alteration that an isolated static medium undergoes, such as the storage rock when it has interaction with a dynamic medium, which is represented by all the operative processes, such as drilling, cementing, firing and production.
TOTAL damage (S)
The pseudo damages that are considered are the following:
- Partial penetration damage
- Deviation damage
- Damage in the vicinity of the well
- Gravel pack damage
- Puncture damage
- Hydraulic fracture damage
The module is currently in the validation stage of the following damages with the respective model:
Daño por penetración parcial
Brons & Marting (1955) Odeh (1980)
Deviation damage
Cinco et al (1975)
Damage in the vicinity of the well
Nutmeg (1937)
Puncture damage
Karakas & Tariq (1991) McLeod (1983)
Nodal Analysis
Formation damage
This module allows you to calculate each of the pseudo damages caused by operational processes, such as drilling, cementing, firing and production.
Capital Analysis
Total damage
This module allows you to calculate each of the pseudo damages caused by operational processes, such as drilling, cementing, firing and production.
The sum of the pseudaños is the total damage of the formation that you can later use in the Nodal Analysis calculation.
Capital Analysis
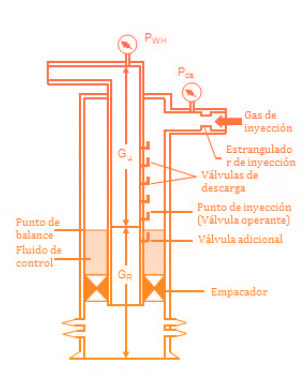
OPERATING VALVE
Assessment of current and future performance according to the operating conditions of the well and the reservoir to obtain the production potential.
For its determination, the gas gradient in the annular space is calculated according to the properties of the gas and the injection pressure at the surface, which is compared with the opening pressures of the valves.
The following methods for calculating the gas gradient are available:

Static gradient

Cullender-Smith (considers friction head losses)
It applies to vertical and deviated wells, with the characteristic that some input parameters can be linked with the data in real time, later the result can be used to perform the Nodal Analysis.
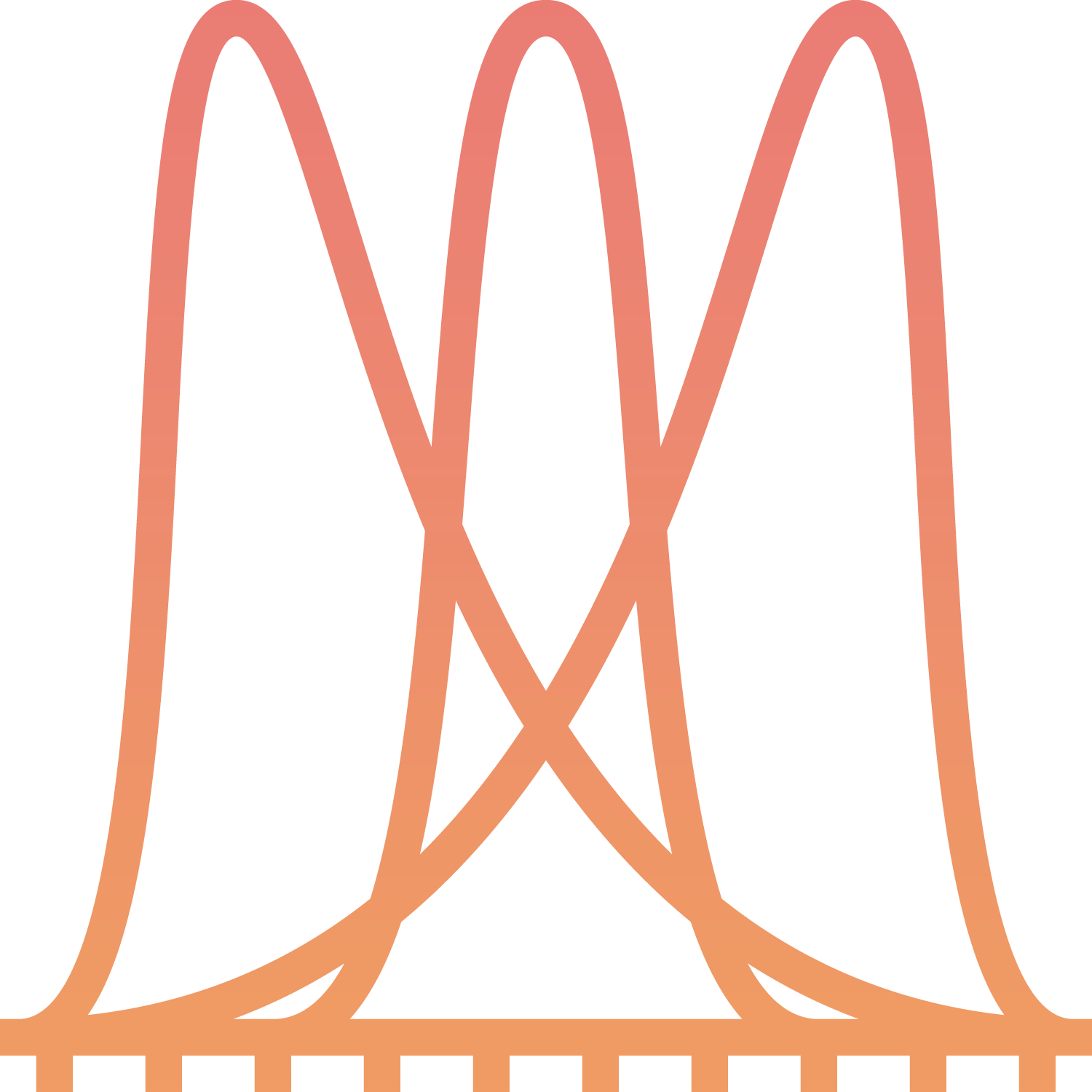
The results are represented graphically (depth vs. pressure).
Capital Analysis
Operating valve
The valve (s) currently operating are determined, in which the gas injection is carried out.
With the injection pressure at the surface, the gas gradient in the annular space is calculated and compared with the opening pressures of the valves in the production line.
The results are visualized in a graph of pressure profiles (depth vs. pressure).
BN diagnosis
If the well has Pneumatic Pumping, the expected production is determined according to current operating conditions.
It allows you to know the behavior of pressures throughout the well.
It is an evaluation prior to the Nodal Analysis.